
The existence of the railways we use every day from home to work, or one of the world’s most visited tourist attraction points Eiffel Tower, is made possible by the use of steel as a structural material. 1.2 The tolerances specified in this standard do not apply to structures like steel railway bridges which require closer tolerances.In today’s world, we see and use steel structures everywhere. AISC Weight the weight of structural steel as defined by the AISC.1.1 This standard covers tolerances on dimensions for fabrication of steel structures manufactured by riveting, bolting or welding. AISC The American Institute of Steel Construction. Usually prepared and provided to the steel mill or manufacturer to reserve a time slot (window) in which the steel order will be produced or to reserve a certain quantity of shapes produced by the mill.
It is designed to have a good strength/weight ratio (which is also called specific strength) and to be cost-effective in order to be benefited as a structural component in buildings, roads, bridges, etc. Specialty Tube Refers to a wide variety of high-quality custom-made tubular products requiring critical tolerances, precise dimensional control and special metallurgical properties.Structural steel is a type of steel that is used as a construction material. 1.) What is structural steel?Category of steel that includes electrical (see Silicon Electrical Steel), alloy (see Alloy Steel), stainless (see Stainless Steel), and tool steels (see Tool Steels). But what exactly is structural steel? What is the difference between mild and structural steel? Why and how do people use it? All of these questions and more will be thoroughly explained in this article.
Steel, one of the most essential materials of the modern world, comes in various different grades and shapes. And of universal mill plates over 36 inches in width , shall conform to. ASTM A36 steel plate is a structural-quality mild carbon steel used in general construction applications including bolted or welded construction of buildings, bridges and common machine parts.( a ) The sectional area or weight of each structural shape , and of each rolled. With mil spec 80 AR15 lower receivers regardless of polymer or metal construction.Because of tolerances, ie ASTM A36 steel plate thickness tolerance, flatness and camber, as well as the hot roll condition, ASTM A36 steel plate generally does not finish to specified thickness.

High Strength Low Alloy Steels:This kind of steels is designed to have better mechanical properties and be more resistant to atmospheric corrosion than carbon steels. It is mostly used in structural pipe and tubing. Carbon steels are generally categorized by their carbon content as low-carbon (< 0.3%), medium-carbon (0.3-0.6%), high carbon (0.6-1%) and ultrahigh carbon (1.25-2%) steels. Here are the standard structural steel materials: Carbon Steels:Steel can be defined as carbon steel when the addition of any other alloying element (such as tungsten, zirconium, cobalt, nickel, etc.) is not required, copper content does not exceed 0.4% or the following elements does not exceed indicated percentages in weight (Mn: 1.6%, Si: 0.6%, Cu: 0.6%) (3). So, different grades of structural steel must be chosen according to different design requirements.Several types of steel can be shaped and used as beams, rods, plates, bars, or profiles.
This process introduces a uniform grain structure to the material, which decreases discontinuity in the matrix by removing voids, gas bubbles and increases overall strength (4). It is done by applying mechanical and thermal energy to steel ingots or billets. Forged Steels:Forging is simply the process of shaping the metal while it is in the solid-state. Mostly used in structural shapes and plates. Weathering steels which are a sub-type of high strength low alloy steels, have high resistance against atmospheric corrosion by forming a passive, rust-like layer on the surface, being one of the important structural steels. Small portions of other alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, nitrogen, vanadium, niobium, and titanium can be used in different combinations to alter the properties (3).

It means that the tolerance against poor foundations is higher. Special names have for all steels.A36 – structural shapes and plate 5.) Advantages and Disadvantages of Structural Steels ADVANTAGESWhen compared, steel dominates every other conventional structural material such as stone, cement, or wood in terms of strength/weight ratio. The four-number AISI steel grades usually used for mechanical engineering, machines, and vehicles are a totally different specification series. While many sections are formed by hot or cold rolling, others are made by welding together flat or bent plates.Figure 2: The Various Types of Structural Steel Shapes b.) ASTMThese steels have associate alloy identification beginning with A and then two, three, or four numbers.
They are both strong and ductile. Structural steels have high toughness values thus they are very suitable for construction applications. High Toughness:The ability of a material to absorb energy is called toughness. Hard and brittle materials can fail suddenly, thus are not favourable. Yielding up to some point prevents premature failures. Thanks to the elastic nature of steel, it can return to its original shape after bending.
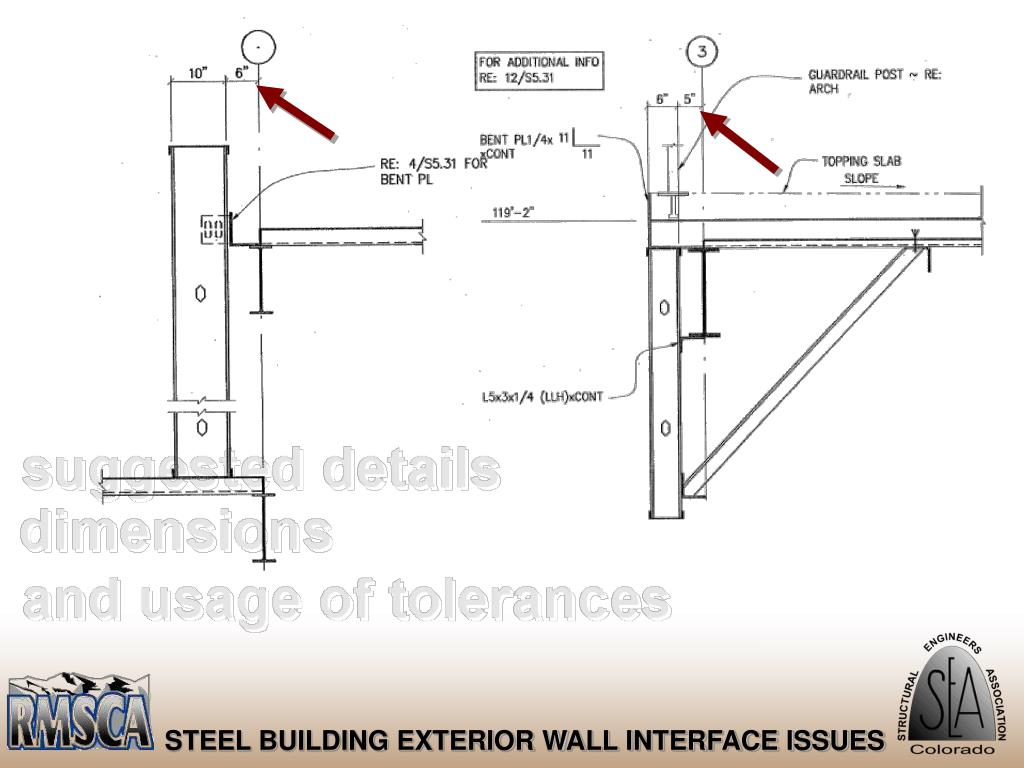
It is generally used in designing and building industrial places. ConstructionStructural steel has varied applications in the construction industry. Due to properties especially highly durable, corrosion-resistant, tensile, and relatively low price has found used in various fields. Structural Steel is that the most preferential metal by architects, designers, engineers, contractors, and fabricators. 6.) Structural Steels ApplicationsWhat comes to your mind when you hear the word structural steel? Hopefully, it’s not just construction.
All workshops, offices, structural parts of mines such as mining screens, fluidized bed boilers, buildings are made with structural steel. Most of the components in the mining substructure are reinforced using structural steel. MiningThe mining industry has a lot of applications of structural steel. Every year, about 25% of structural steels are used in the construction of buildings. Steel frames, beams, columns, bars, girders, plates, and many others are created by structural steel fabricators which are used in the construction industry.
MarineMost marine vehicles are built using structural steel, for example submarines, boats, supertankers, ladders, steel flooring, and grating, stairs, and fabricated sections of steel. Structural steels used due to their elasticity, corrosion resistance, tensile strength, ductility, malleability, and affordability. Most of these vehicles contain a significant amount of structural steel. Therefore, do not interfere with other elements TransportationStructural steel is used to produce trucks, transmissions, trains, rails and ships, anchor chains, aircraft undercarriages, and jet engine components.
In most cases, standards give mainly the basic requirements such as limits on chemical composition and tensile properties.The two most widespread standards of use are the European Standard (EN 10025) and the American Standard (ASTM). Structural steels are generally specified based on the appropriate industry or national standards, such as ASTM, API, BSI, ISO, etc. 7.) StandartsStructural steel shapes, sizes, chemical composition, mechanical properties like strengths, storage practices are manufactured by standards. It is used in many industrial buildings in renewable and non-renewable energy sources such as transmission towers, pipelines, wind turbines, electromagnets, transformer cores, oil and gas wells. EnergyThere are a lot of structural steel applications in the energy industry. These properties make structural steels purposive for the marine sector.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
